Search results
- DictionaryDis·ease/dəˈzēz/
noun
- 1. a disorder of structure or function in a human, animal, or plant, especially one that has a known cause and a distinctive group of symptoms, signs, or anatomical changes: "bacterial meningitis is a rare disease"
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms.
Go to: Summary. Disease, disability and their definitions. At first sight, the answer to “What is a disease?” is straightforward. Most of us feel we have an intuitive grasp of the idea, reaching mentally to images or memories of colds, cancer or tuberculosis.
- Jackie Leach Scully
- 10.1038/sj.embor.7400195
- 2004
- EMBO Rep. 2004 Jul; 5(7): 650-653.
Human disease, an impairment of the normal state of a human being that interrupts or modifies vital functions. Disease may be trivial if the impairment is minimal. It may also be associated with illness or be latent, becoming apparent at some later time.
B1. an illness caused by an infection or by a failure of health and not by an accident: heart disease. an infectious disease. Fewer examples. an incurable disease. Eating fatty food increases the risk of heart disease. The disease affects both humans and animals. As many as 6000 people may have been infected with the disease.
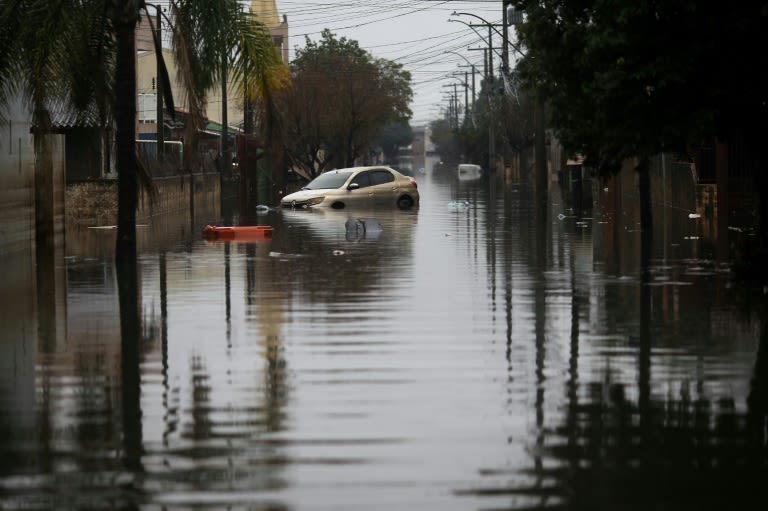
News about landslide, Brazil, disease outbreak
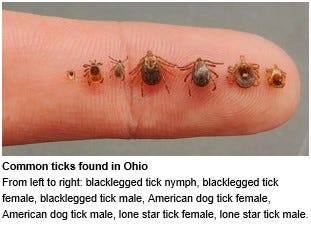
News about Lyme disease, Ohio, ticks
News about coal miners, Insmed, black lung benefits
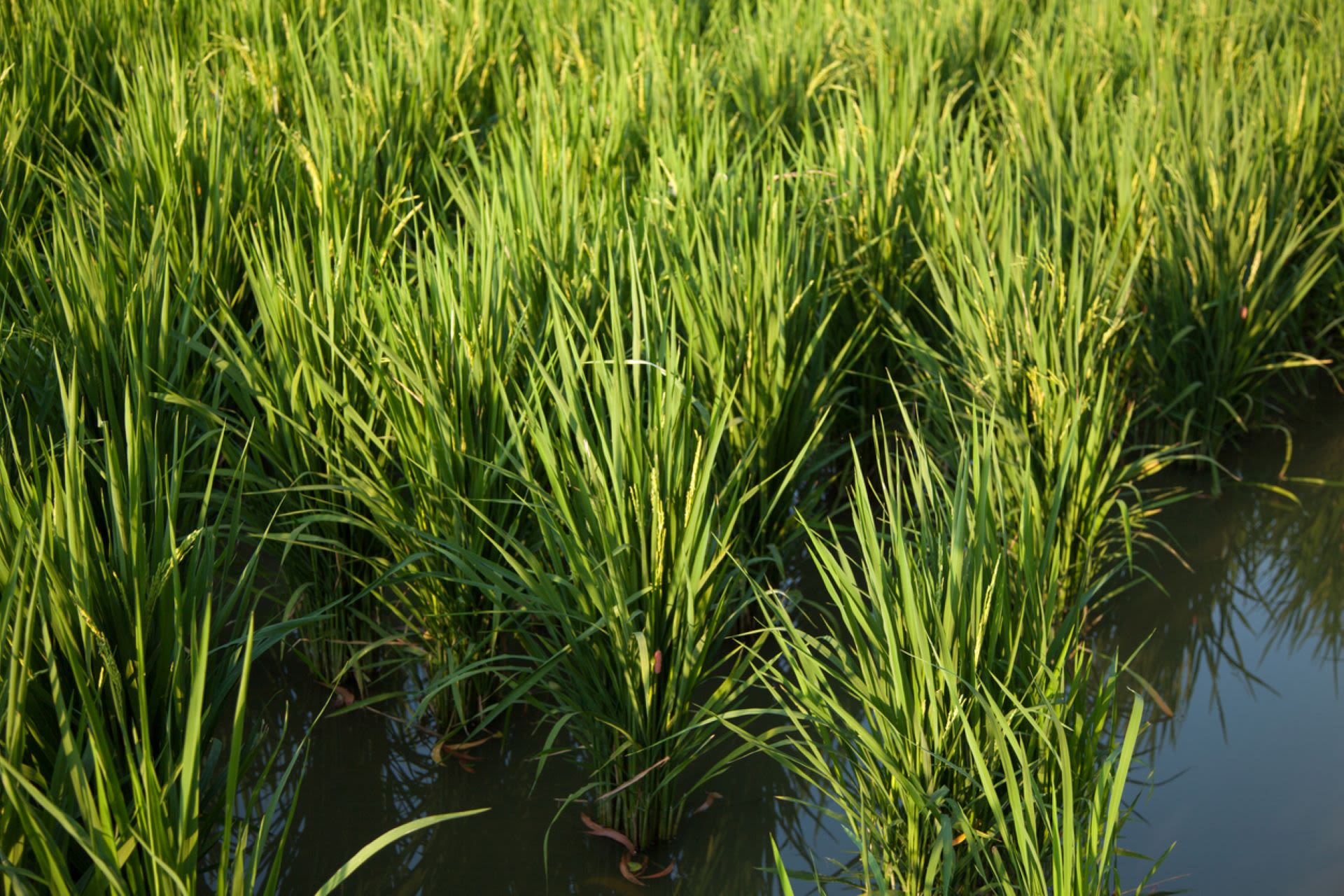
News about Alzheimer's disease, rice blast disease, gospel singer
noun. a disordered or incorrectly functioning organ, part, structure, or system of the body resulting from the effect of genetic or developmental errors, infection, poisons, nutritional deficiency or imbalance, toxicity, or unfavorable environmental factors; illness; sickness; ailment.
Sep 22, 2008 · Back to Top. Concepts of Disease and Health. First published Mon Sep 22, 2008; substantive revision Wed Mar 18, 2020. Health and disease are critical concepts in bioethics with far-reaching social and political implications.
Sep 27, 2020 · Disease is an objective term which implies a malfunctioning of the body or part of the body. Disease is pathological and is diagnosed on the basis of recognizable signs and symptoms. Illness is the subjective experience of pain, discomfort or disorder.