Search results
Jul 27, 2006 · First, it proposes a definition of democracy. Second, it outlines different approaches to the question of why democracy is morally valuable at all. Third, it discusses the issue of whether and when democratic institutions have authority and different conceptions of the limits of democratic authority.
News about Donald Trump, Robert De Niro, Daily Show
News about democracy, America, competition
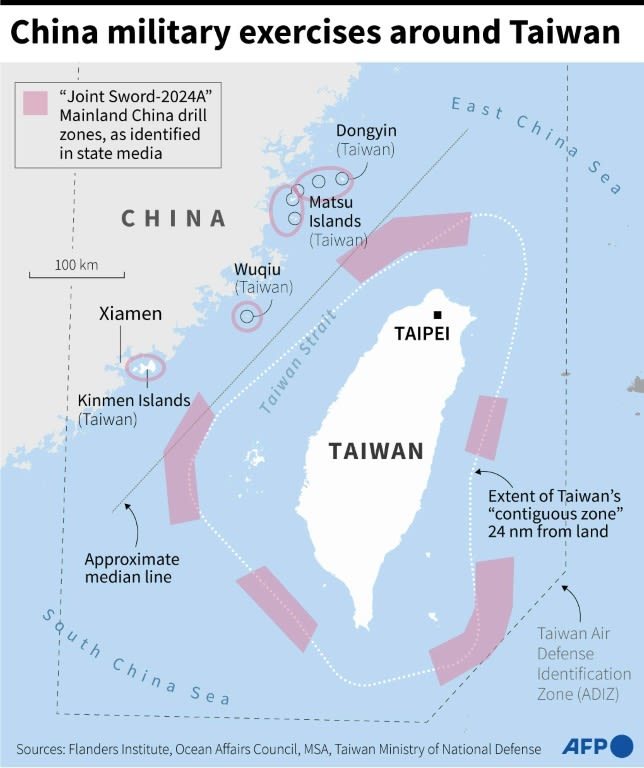
News about Taiwan, China, military exercises
Also in the news
May 6, 2024 · Democracy is a system of government in which power is vested in the people and exercised by them directly or through freely elected representatives. The term is derived from the Greek ‘demokratia,’ which was coined in the 5th century BCE to denote the political systems of some Greek city-states, notably Athens.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to democracy. Democracy – form of government which allows people to participate equally—either directly or through elected representatives—in the proposal, development, and creation of laws .
Solon (in 594 BC), Cleisthenes (in 508–07 BC), and Ephialtes (in 462 BC) contributed to the development of Athenian democracy. Cleisthenes broke up the unlimited power of the nobility by organizing citizens into ten groups based on where they lived, rather than on their wealth. [5]
What is democracy? Where was democracy first practiced? How is democracy better than other forms of government? Why does democracy need education? What is Pericles remembered for?
Representative democracy (also called electoral democracy or indirect democracy) is a type of democracy where representatives are elected by the public.
Democracy is the opposite of a dictatorship. Dictatorships often act against freedom of expression so people cannot say bad things about the dictator or replace them for somebody else. An important source of information is the Democracy Index published by the Economist periodical.