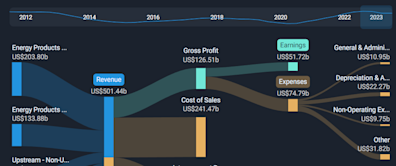
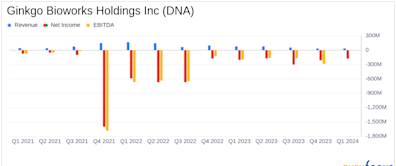
Search results
- 0.6249Add to watchlist-0.0362 (-5.48%)At close: Tue. May 28, 2024 4:00 PM EDT · Nasdaq Real Time Price (USD) · Market closed
- Open0.6741High0.6790Low0.6139
- Mkt Cap1.38BP/E (TTM)N/ADiv & YieldN/A & N/A
- Prev. Close0.661152 Wk. Low0.613952 Wk. High2.5450
Top storiesGinkgo Bioworks Holdings First Quarter 2024 Earnings: EPS Beats Expectations, Revenues LagYahoo Finance · 3 weeks agoGinkgo Bioworks Holdings, Inc. (NYSE:DNA) Q1 2024 Earnings Call TranscriptYahoo Finance · 3 weeks agoGinkgo Bioworks Holdings Inc (DNA) Reports Q1 2024 Results: A Comprehensive OverviewYahoo Finance · 3 weeks agoRelated stocks
DNA exists in many possible conformations that include A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA forms, although only B-DNA and Z-DNA have been directly observed in functional organisms. The conformation that DNA adopts depends on the hydration level, DNA sequence, the amount and direction of supercoiling, chemical modifications of the bases, the type and ...
May 15, 2024 · DNA, organic chemical of complex molecular structure found in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It codes genetic information for the transmission of inherited traits. The structure of DNA was described in 1953, leading to further understanding of DNA replication and hereditary control of cellular activities.
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
- What does DNA do?Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is an organic chemical that contains genetic information and instructions for protein synthesis. It is found in most ce...
- What is DNA made of?DNA is made of nucleotides. A nucleotide has two components: a backbone, made from the sugar deoxyribose and phosphate groups, and nitrogenous base...
- Who discovered the structure of DNA?The discovery of DNA’s double-helix structure is credited to the researchers James Watson and Francis Crick, who, with fellow researcher Maurice Wi...
- Can you edit DNA?Gene editing today is mostly done through a technique called Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR), adopted from a bac...
- What’s the difference between DNA and RNA?DNA is the master blueprint for life and constitutes the genetic material in all free-living organisms. RNA uses DNA to code for the structure of p...
- Overview
- For more information about DNA:
- Topics in the Cells and DNA chapter
- GeneratedCaptionsTabForHeroSec
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). Mitochondria are structures within cells that convert the energy from food into a form that cells can use.
The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to the way in which letters of the alphabet appear in a certain order to form words and sentences.
DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Together, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat like a ladder, with the base pairs forming the ladder’s rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder.
An important property of DNA is that it can replicate, or make copies of itself. Each strand of DNA in the double helix can serve as a pattern for duplicating the sequence of bases. This is critical when cells divide because each new cell needs to have an exact copy of the DNA present in the old cell.
DNA is a double helix formed by base pairs attached to a sugar-phosphate backbone.
Credit: U.S. National Library of Medicine
The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), provides a fact sheet Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) that gives an introduction to this molecule.
StatedClearly offers a video introduction to DNA and how it works.
The New Genetics, a publication of the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, part of the NIH, discusses the structure of DNA and how it was discovered.
A basic explanation and illustration of DNA can be found on Arizona State University's "Ask a Biologist" website.
The Virtual Genetics Education Centre, created by the University of Leicester, offers additional information on DNA, genes, and chromosomes.
An overview of mitochondrial DNA is available from the Neuromuscular Disease Center at Washington University in St. Louis.
•What is a cell?
•What is DNA?
•What is a gene?
•What is a chromosome?
•How many chromosomes do people have?
•What is noncoding DNA?
Learn about the structure, function, and inheritance of DNA, the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Find out how DNA is made up of four chemical bases, forms a double helix, and can replicate itself.
Learn how DNA is a complex molecule that encodes biological information for all living organisms. Explore the structure, components, and function of DNA, as well as its role in inheritance and evolution.
Aug 24, 2020 · Each DNA sequence that contains instructions to make a protein is known as a gene. The size of a gene may vary greatly, ranging from about 1,000 bases to 1 million bases in humans. Genes only make up about 1 percent of the DNA sequence. DNA sequences outside this 1 percent are involved in regulating when, how and how much of a protein is made.
People also ask
What does the DNA do?
What is DNA and how does it work?
What is the function of the DNA?
Apr 8, 2019 · DNA Definition. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. DNA is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, are mostly present inside the ...
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.