Search results
News about SpaceX, Falcon 9, China
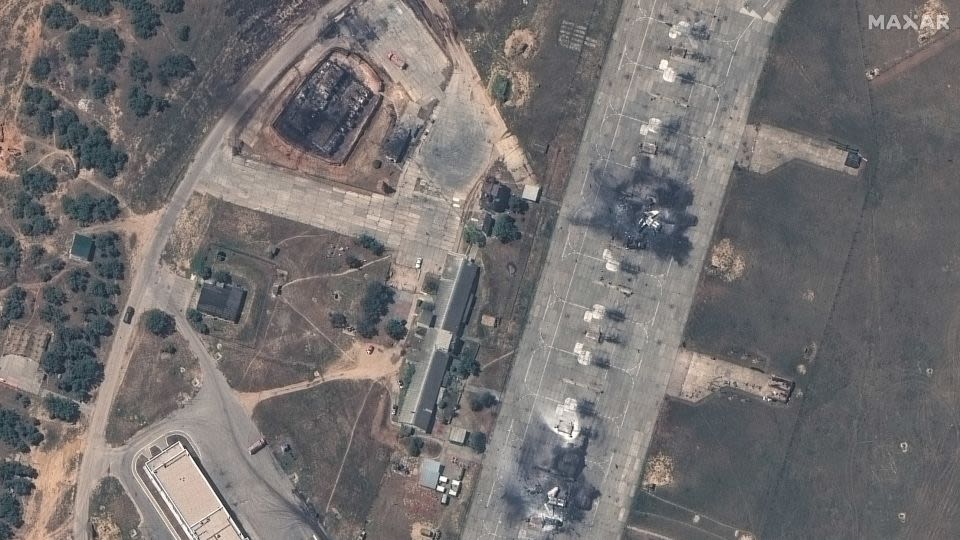
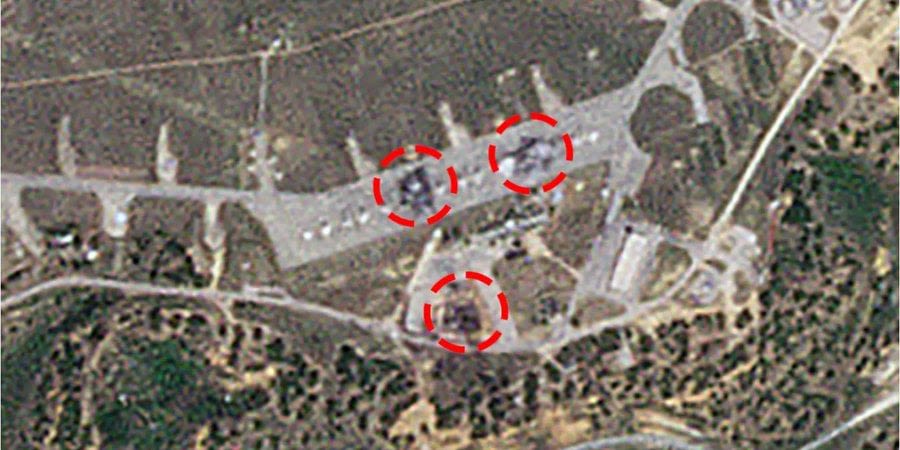
News about satellite images, Belbek airfield, destroyed jets
News about satellite texting, AT&T, Android 15
Also in the news
Sep 5, 2018 · A satellite is a body that orbits around another body in space. There are two different types of satellites – natural and man-made. Examples of natural satellites are the Earth and Moon. The Earth rotates around the Sun and the Moon rotates around the Earth.
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geopositioning. A satellite navigation system with global coverage is termed global navigation satellite system ( GNSS ). As of 2023, five global systems are operational: the United States 's Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia 's Global ...
Global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are invisible pieces of technology that people rely on everyday without thinking about it. From communications systems to mobile navigation applications like Google Maps, GNSS affects what we do every day. But what are global navigation satellite systems?
Jun 6, 2022 · Last updated: June 6, 2022. Eyes in the sky, space mirrors bouncing phone calls round Earth, heavenly compasses helping us home—these are just three of the things that satellites do for us. When you gaze through the clouds on a brilliant blue day, you might catch sight of a plane or two leaving vapor trails in its wake.
Mar 22, 2023 · The 5 main types of satellites based on their orbits are: low Earth orbit (LEO); medium Earth orbit (MEO); geostationary orbit (GEO); Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO); geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). Let’s dig deeper into the nature of these 5 different types of satellites’ orbits to learn more about their characteristics and potential uses.
A satellite is basically a self-contained communications system with the ability to receive signals from Earth and to retransmit those signals back with the use of a transponder —an integrated receiver and transmitter of radio signals.
Jan 13, 2021 · NASA is developing capabilities that will allow missions at high altitudes to take advantage of signals from Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) constellations — like GPS commonly used in the U.S.