Search results
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. [1] Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. [2] [3] Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity.
- Virus (Disambiguation)
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates...
- Coronavirinae
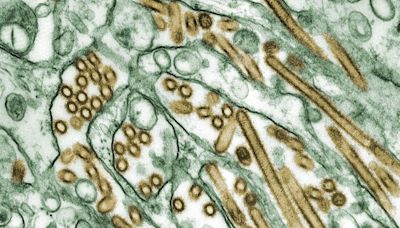
Etymology. The name "coronavirus" is derived from Latin...
- Computer Virus
Hex dump of the Brain virus, generally regarded as the first...
- Riboviria
Etymology. Riboviria is a portmanteau of ribo, referencing...
- Infectious Agent
Pathogenicity. Pathogenicity is the potential...
- Dmitri Ivanovsky
In 1898, the Dutch microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck...
- Introduction to Viruses
Introduction to viruses. A virus is a tiny infectious agent...
- History
Electron micrograph of the rod-shaped particles of tobacco...
- Duplodnaviria
Duplodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all...
- Viral Disease
Viral disease. A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs...
- Virus (Disambiguation)
Introduction to viruses. A virus is a tiny infectious agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected, the host cell is forced to rapidly produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus. Unlike most living things, viruses do not have cells that divide; new viruses assemble in the infected host cell.
A virus is a tiny parasite. [1] Virology is the study of viruses. Viruses can only be seen under an electron microscope. Viruses are not free-living: they can only be parasites. They always reproduce inside other living things. All viruses infect living organisms, and may cause disease.
- LinearCircularSegmented
Viral disease. A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells. [1] Examples are the common cold, gastroenteritis and pneumonia. [2]
TypeFamilyTransmissionDiseasesdroplet contact fecal-oral venereal ...gastroenteritis keratoconjunctivitis ...fecal-oral respiratory droplet contactHand, foot and mouth disease pleurodynia ...vertical transmission bodily fluidsinfectious mononucleosis Cytomegalic ...salivainfectious mononucleosis Burkitt's ...Apr 12, 2024 · Learn about virus, a small infectious agent that can multiply only in living cells of animals, plants, or bacteria. Explore the history, classification, structure, and functions of viruses, as well as their applications and ecological significance.
- What is a virus?A virus is an infectious agent of small size and simple composition that can multiply only in living cells of animals, plants, or bacteria.
- What are viruses made of?A virus particle is made up of genetic material housed inside a protein shell, or capsid. The genetic material, or genome, of a virus may consist o...
- What size are viruses?Most viruses vary in diameter from 20 nanometres (nm; 0.0000008 inch) to 250–400 nm. The largest viruses measure about 500 nm in diameter and are a...
- Are all viruses spherical in shape?Shapes of viruses are predominantly of two kinds: rods (or filaments), so called because of the linear array of the nucleic acid and the protein su...
- Why are some viruses dangerous?When some disease-causing viruses enter host cells, they start making new copies of themselves very quickly, often outpacing the immune system’s pr...
Learn what a virus is, how it infects a cell, and how it differs from bacteria. Explore the structure, diversity, and evolution of viruses with examples and interactive features.
People also ask
Which viruses infect humans that have not been associated with disease?
What is a virus in biology?
What is the structure of a virus?
What is a virus called?
Oct 19, 2023 · Learn about viruses, their structure, replication, and effects on living hosts. Find out how viruses can be used for gene therapy and how they differ from bacteria and antibiotics.