Search results
416
- A former minister of education in Japan, Kikuchi said that the first earthquake in Japan's recorded history occurred in 416.
www.npr.org › 2011/03/13 › 134475802
People also ask
When was the first earthquake in Japan?
What was the 'great earthquake of East Japan'?
What happened in Japan after a record earthquake and tsunami?
What happened during the 2011 Tohoku earthquake & tsunami?
Mar 13, 2011 · A former minister of education in Japan, Kikuchi said that the first earthquake in Japan's recorded history occurred in 416. The bulk of Kikuchi's address explained his country's...
The date was September 1, 1923, and the event was the Great Kanto Earthquake, at the time considered the worst natural disaster ever to strike quake-prone Japan. The initial jolt was...
News about Q1 2024, insured losses, economic losses
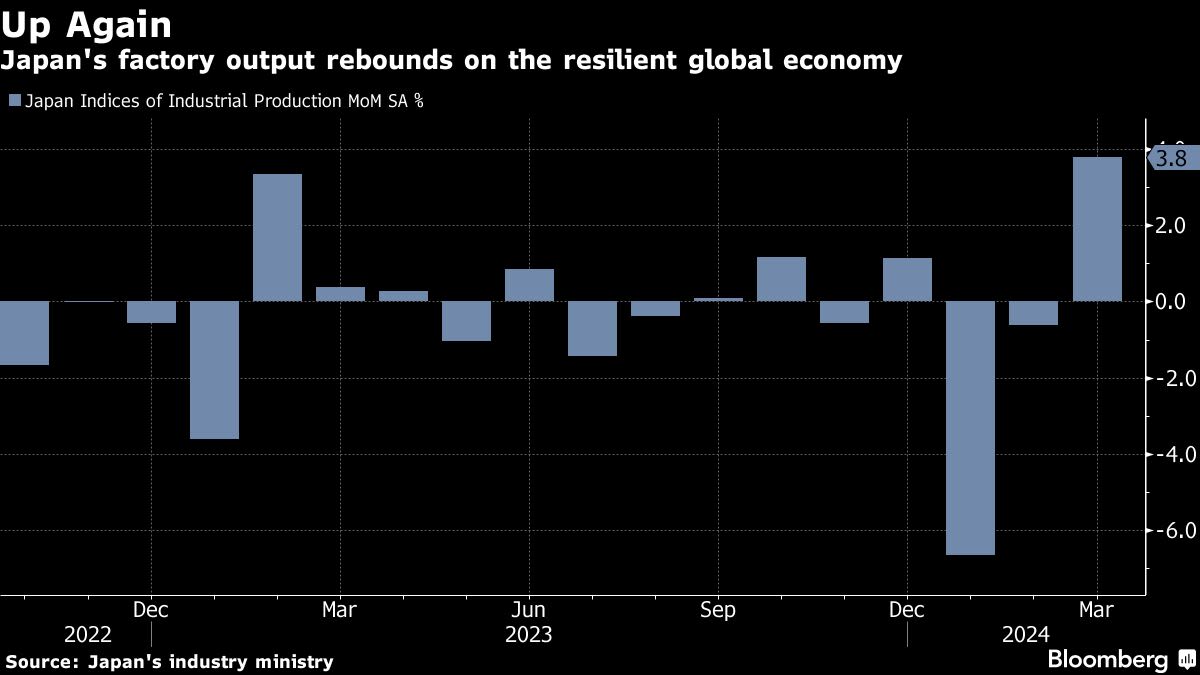
News about Japan, Passover, factory output
News about 6.5-magnitude earthquake, Japanese island region, tsunami
Also in the news
Aug 28, 2023 · 1923. Japan’s Great Kanto Earthquake kills over 140,000. On September 1, 1923, a routine lunch hour in Japan's capital city of Tokyo and neighboring “City of Silk” Yokohama is disrupted when a...
On 11 March 2011, at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC ), a Mw 9.0–9.1 undersea megathrust earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, 72 km (45 mi) east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region. It lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami.
- 6 minutes
- 2011-03-11 05:46:24
- 11 March 2011
- 14:46:24 JST
- A Surprise Disaster
- The 2011 Tohoku Earthquake
- Early Warning
- Death Toll of The 2011 Earthquake and Tsunami
- The Fukushima Nuclear Meltdown
- The Response
- Worldwide Effects
- Amazing Facts
- Additional Resources
- Bibliography
The unexpected disaster was neither the largest nor the deadliest earthquake and tsunamito strike this century. That record goes to the 2004 Banda Aceh earthquake and tsunami in Sumatra, a magnitude-9.1, which killed more than 230,000 people. But Japan's one-two punch proved especially devastating for the earthquake-savvy country, because few scien...
The 2011 Tohoku earthquake struck offshore of Japan, along a subduction zone where two of Earth's tectonic platescollide. In a subduction zone, one plate slides beneath another into the mantle, the hotter layer beneath the crust. The great plates are rough and stick together, building up energy that is released as earthquakes. East of Japan, the Pa...
Residents of Tokyo received a minute of warning before the strong shaking hit the city, thanks to Japan's earthquake early warning system. The country's stringent seismic building codes and early warning system prevented many deaths from the earthquake, by stopping high-speed trains and factory assembly lines. People in Japan also received texted a...
The number of confirmed deaths is 19,747 as of December, 2021, according to the reconstruction agency. More than 2,500 people are still reported missing. Less than an hour after the earthquake, the first of many tsunami waves hit Japan's coastline. The tsunami waves reached run-up heights (how far the wave surges inland above sea level) of up to 12...
The tsunami caused a cooling system failure at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, which resulted in a level-7 nuclear meltdown and release of radioactive materials. The electrical power and backup generators were overwhelmed by the tsunami, and the plant lost its cooling capabilities. "Fukushima was created by the tsunami. The earthquake wa...
In the tsunami's aftermath, Japan's Meteorological Agency was criticized for issuing an initial tsunami warning that underestimated the size of the wave. In some regions, such as Miyagi and Fukushima, only 58% of people headed for higher ground immediately after the earthquake, according to a Japanese government study published in August 2011. Many...
The tsunami waves also traveled across the Pacific, reaching Alaska, Hawaii and Chile. In Chile, some 11,000 miles (17,000 km) distant, the tsunami was 6.6 feet (2 meters) high when they reached the shore, according to the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center. Related: Weird Earth Movement After Japan Earthquake Finally Explained The surge of water carri...
Here are some of the amazing facts about the Japan earthquake and tsunami. 1. The earthquake shifted Earth on its axis of rotation by redistributing mass, like putting a dent in a spinning top. The temblor also shortened the length of a day by about a microsecond. 2. More than 5,000 aftershocks hit Japan in the year after the earthquake, the larges...
Vasily Titov, Chief Scientist of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Center for Tsunami Research in Seattle, Washington. “Status of Reconstruction and Reconstruction Efforts.” Japan Reconstruction Agency, Dec. 2021. https://www.reconstruction.go.jp/english/ P.M. Fulton et al. “Low Coseismic Friction on the Tohoku-Oki Fault ...
Mar 13, 2011 · STORY HIGHLIGHTS. Moments of the quake from the first strike to tsunami hit. Concerns now of damage of nuclear power plants. Earthquake was the largest in Japanese history. (CNN) -- Here's a...
Mar 11, 2011 · Fri 11 Mar 2011 10.55 EST. What caused the tsunami? The most powerful earthquake recorded in Japanese history, magnitude 8.9. The tremors were the result of a violent uplift of the sea...