Search results
Most Recent Earthquakes Worldwide
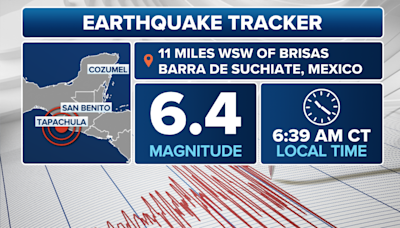
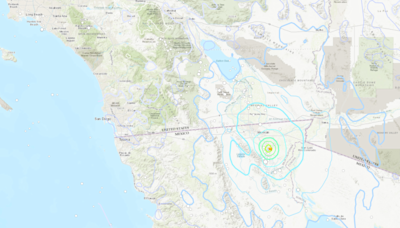
earthquake.usgs.govMagnitudeLocationTimeM5.217 hours agoM5.220 hours agoM5.31 day agoM5.21 day agoM5.21 day agoM5.91 day agoM6.42 days agoM5.42 days agoView the map of the latest earthquakes around the world, updated in real time by the USGS. See the location, magnitude, depth, and time of each earthquake, as well as the distance from your current location.
- Latest Earthquakes - USGS
Search Earthquake Catalog Time Zone. Display event dates and...
- Latest Earthquakes | U.S. Geological Survey - USGS.gov
The Latest Earthquake web application displays information...
- Latest Earthquakes - USGS
- Overview
- Causes of earthquakes
- GeneratedCaptionsTabForHeroSec
Over the centuries, earthquakes have been responsible for millions of deaths and an incalculable amount of damage to property. Depending on their intensity, earthquakes (specifically, the degree to which they cause the ground’s surface to shake) can topple buildings and bridges, rupture gas pipelines and other infrastructure, and trigger landslides, tsunamis, and volcanoes. These phenomena are primarily responsible for deaths and injuries. Very great earthquakes occur on average about once per year.
What are earthquake waves?
Earthquake waves, more commonly known as seismic waves, are vibrations generated by an earthquake and propagated within Earth or along its surface. There are four principal types of elastic waves: two, primary and secondary waves, travel within Earth, whereas the other two, Rayleigh and Love waves, called surface waves, travel along its surface. In addition, seismic waves can be produced artificially by explosions.
How is earthquake magnitude measured?
Magnitude is a measure of the amplitude (height) of the seismic waves an earthquake’s source produces as recorded by seismographs. Seismologist Charles F. Richter created an earthquake magnitude scale using the logarithm of the largest seismic wave’s amplitude to base 10. Richter’s scale was originally for measuring the magnitude of earthquakes from magnitudes 3 to 7, limiting its usefulness. Today the moment magnitude scale, a closer measure of an earthquake’s total energy release, is preferred.
Where do earthquakes occur?
Earth’s major earthquakes occur mainly in belts coinciding with the margins of tectonic plates. This has long been apparent from early catalogs of felt earthquakes and is even more readily discernible in modern seismicity maps, which show instrumentally determined epicentres. The most important earthquake belt is the Circum-Pacific Belt, which affects many populated coastal regions around the Pacific Ocean—for example, those of New Zealand, New Guinea, Japan, the Aleutian Islands, Alaska, and the western coasts of North and South America. It is estimated that 80 percent of the energy presently released in earthquakes comes from those whose epicentres are in this belt. The seismic activity is by no means uniform throughout the belt, and there are a number of branches at various points. Because at many places the Circum-Pacific Belt is associated with volcanic activity, it has been popularly dubbed the “Pacific Ring of Fire.”
Britannica Quiz
April Showers to March’s Lions and Lambs
A second belt, known as the Alpide Belt, passes through the Mediterranean region eastward through Asia and joins the Circum-Pacific Belt in the East Indies. The energy released in earthquakes from this belt is about 15 percent of the world total. There also are striking connected belts of seismic activity, mainly along oceanic ridges—including those in the Arctic Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, and the western Indian Ocean—and along the rift valleys of East Africa. This global seismicity distribution is best understood in terms of its plate tectonic setting.
Learn about earthquakes, the sudden shaking of the ground caused by the passage of seismic waves through Earth's rocks. Find out how earthquakes occur, where they occur, and how they are measured by seismology.
An earthquake – also called a quake, tremor, or temblor – is the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves.
Find information on recent or historic earthquakes, maps, lists, statistics, and resources by state or worldwide. Learn about earthquake hazards, effects, and how to report or get notified of earthquakes.
Oct 19, 2023 · Hundreds of earthquakes occur on Earth everyday. Most of them are small, barely detectable by most people. But occasionally there is a much more significant quake. On average, a major earthquake —one with a magnitude of 7.0-7.9—strikes somewhere on the planet more than once a month.
Feb 6, 2023 · Learn about the science of earthquakes, how they occur along fault zones, and how they are measured by magnitude ratings. Find out the types of faults, the strongest quakes ever recorded, and the effects of earthquakes on people and the environment.
People also ask
What are the effects of earthquakes?
How do earthquakes happen?
How many kilometers away from Neiafu was the earthquake?
How do scientists study earthquakes?