- CHD +0.11%
Search results
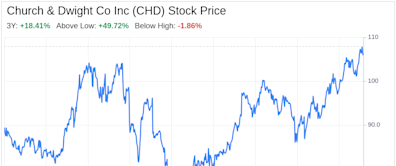
- 106.51Add to watchlist+0.12 (+0.11%)At close:4:00 PM EDTMon. May 20, 2024106.51 0.00 (0.00%)After hrs:7:50 PM EDTMon. May 20, 2024Nasdaq Real Time Price (USD) · Market closed
- Open106.37High106.60Low105.84
- Mkt Cap26.04BP/E (TTM)33.71Div & Yield1.14 & 1.07%
- Prev. Close106.3952 Wk. Low82.2552 Wk. High108.68
What analysts are sayingTop storiesChurch & Dwight Co Inc's Dividend AnalysisYahoo Finance · 1 week ago- CHD +0.11%
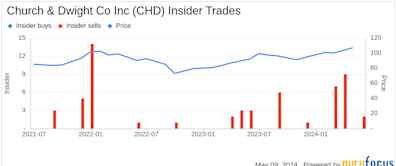
Insider Sale: Director Robert Shearer Sells 13,200 Shares of Church & Dwight Co Inc (CHD)Yahoo Finance · 2 weeks ago- CHD +0.11%
Decoding Church & Dwight Co Inc (CHD): A Strategic SWOT InsightYahoo Finance · 3 weeks agoRelated stocks
Flights
Powered by
Congenital heart defects are abnormalities of the heart structure or function that are present at birth. They can include heart valve defects, atrial and ventricular septa defects, stenosis, heart muscle abnormalities and other defects that can prove dangerous or even deadly. Learn more about CHD.
- What Are The Symptoms?
- What Causes Congenital Heart Disease?
- What Are The Complications of Congenital Heart Disease?
Congenital heart disease symptoms may start as soon as a baby is born or may not appear until later in life. They can include: 1. Cyanosis(bluish skin, lips or nails). 2. Excessive sleepiness. 3. Fast breathing or trouble breathing. 4. Fatigue(extreme tiredness). 5. Getting unusually tired or out of breath during exercise. 6. Heart murmur(a swishin...
CHD happens when the fetal heart doesn’t develop correctly in the uterus. Scientists don’t fully understand why that happens, but it may be related to: 1. Having abnormal chromosomesor genetics that come from parents or happen randomly. 2. Drinking alcohol, smoking or breathing in secondhand smoke during pregnancy. 3. Taking medications during preg...
Congenital heart defects can make you more likely to have: 1. Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). 2. Heart failure. 3. Kidney disease. 4. Blood clots. 5. Pulmonary hypertension. 6. Endocarditis. 7. Liver disease. 8. Speech issues. 9. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Apr 6, 2024 · Symptoms also may return years after a congenital heart defect is treated. Common congenital heart disease symptoms in adults include: Irregular heartbeats, called arrhythmias. Blue or gray skin, lips and fingernails due to low oxygen levels. Depending on the skin color, these changes may be harder or easier to see.
Congenital heart defect. A congenital heart defect ( CHD ), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. [7] A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. [10]
- Often unknown
- Rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, feeling tired
- 303,300 (2015)
Apr 6, 2024 · Tests to diagnose or confirm congenital heart disease in adults include: Electrocardiogram (ECG). This quick test records the electrical activity of the heart. It shows how the heart is beating. Sticky patches with sensors called electrodes attach to the chest and sometimes the arms or legs. Wires connect the patches to a computer, which prints ...
People with a CHD can develop other health problems over time, depending on their specific heart defect, the number of heart defects they have, and the severity of their heart defect. For example, some other health problems that might develop include irregular heart beat (arrhythmias), increased risk of infection in the heart muscle (infective ...
The type of care required is based on the type of CHD a person has. People with simple types of CHD can generally be cared for by a community adult cardiologist. Those with more complex types of CHD will need to be cared for at a center that specializes in adult congenital heart disease, like the Philadelphia Adult Congenital Heart Center.